Fuel injection is a technology used in automobiles that eliminate the need for carburetors. The technology assists the engine in supplying fuel directly to the cylinder in the intake manifold, or in other words, it supplies fuel directly to the engine.
From April 2020, India is adhering to Bharat Stage 6 emission standards. As a result, all motorcycles and scooters have also converted to fuel injection, eliminating the need for traditional carburetors.
What is Fuel Injection
Fuel injection technique is one in which fuel delivers directly to the cylinder in the intake chamber. Sensors in such engines regulate the flow of fuel injected and keep it at proper levels.
As long as the sensors (usually electronic) are functioning properly, the chances of a breakdown or a chock are greatly reduced. There are also various types of fuel injection systems, such as throttle body fuel injection systems and single point fuel injection systems.
The throttle body system delivers fuel directly to the intake chamber from throttle bodies, whereas single point systems deliver fuel from a single injector.
Whatever type of fuel injection uses, it results in crisper throttle response and a more engaging ride overall. In addition, fuel injection systems improve fuel efficiency.
Read Also: Best Mileage Bikes In India 2022
How does Fuel Injection work
The fuel injector is a valve that can open and close several times per second. Springs or an ECU (Electronic Control Unit) control it. The fuel draws from the tank and delivered to the injectors. Transportation accomplishes through the use of fuel lines.
Once the fuel reaches the injector, it pressurizes to the proper level by a fuel pressure regulator. After that, the fuel divides into several cylinders. Following this, fuel spray onto the combustion chamber is the final step.
Fuel injectors are classified into two types:
Mechanical Fuel Injector
The primary mechanism used here to inject fuel is similar to carburetor systems used in the past. That is why many people still confuse it with carbureted engines, but there is a significant difference between these two. While the carburetted system draws low-pressure fuel from the fuel tank, mechanical fuel injector systems draw high-pressure fuel from the tank. This is the basic principle of how mechanical fuel injectors work.
The fuel enters the accumulator after the pumping from the fuel tank. Consider an accumulator to be a buffer for temporary fuel storage. The system’s metering control unit then enters the picture. Its function is to distribute fuel to the cylinders. In this case, getting the right amount of fuel into the right cylinders at the right time is critical.
The fuel and air must precisely mix inside the cylinder, with the correct amount of both. This accomplishes using the flap valve, which is located inside the engine’s air intake. It allows the fuel to flow in the proper direction so that it can mix with the appropriate amount of air. When we increase or decrease the speed of the vehicle. The flap valve opens more or less, and the fuel distributor does the same. As a result, both remain in proportion.
Two springs give power to The system. One is known as the mainspring, and the other as the plunger spring. The mainspring’s job is to control the fuel inlet to the fuel injector; the fuel coming from the fuel pump pressurizes, and this pressure causes the mainspring to open and allow the fuel inside the fuel injector.
As the fuel mixes with the air in the inlet, the pressure rises, causing the plunger spring to move to and fro. This allows the plunger to move outward and the nozzle to open, resulting in the controlled spray of fuel. As you can see, the mechanism used here is spring-loaded, which is why many technicians refer to mechanical injectors as spring-loaded injectors.
Once the fuel injection for a given cycle is complete, the pressure decreases, and the plunger that helps to push outward stops experiencing pressure and returns to its initial position, in compliance with the control unit’s input. This causes the spray to seize, and thus the fuel pumping halted for that cycle.
Read Also: Best Car Washer for the Cleaning of your Car
Electronic Fuel Injector
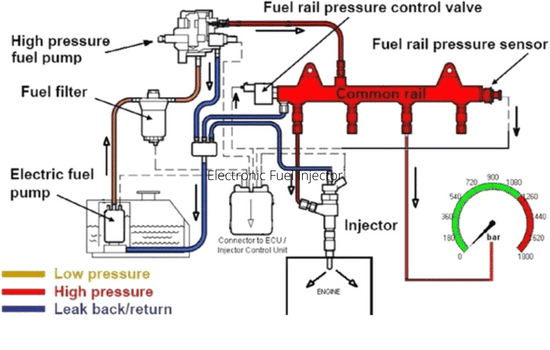
This is a relatively new implementation of the fuel injectors, as many new cars equip now with this system. The basic principle of how these mechanical systems work is the same as described above in Mechanical Fuel Injector. However, they differ in two ways. Specifically, the amount of fuel and the tension used to open and close the valve using the spring. Instead of using these two functions to control the spray of fuel, electronic systems use an electronic control unit that controls all of the required functions.
Air temperature, air intake pressure, engine temperature, engine speed, and accelerator position are all monitored by sensors. All of these connections to the ECU and the current data are sent to it in real-time.
It calculates the specific amount of fuel that needs to enter the cylinders based on the conditions and the ECU’s calculations. All of this information is fed into the ECU in real-time. The processing is so fast that the extent to which valves must open calculates nearly simultaneously.
Fuel rails use to transfer fuel from the fuel tank to the fuel injector. Inside the fuel rails, constant pressure maintains, and an electric fuel pump gets installed to allow fuel to travel through the rails and into the fuel injector.
The ECU calculates the amount of fuel that needs to spray and the number of valves that need to open as the data is fed to it. When electronic signals pass from the ECU to the fuel injector pins. Which are with the wire to a battery and an ignition. An electromagnet inside the fuel injector creates, causing the plunger to move outwards, allowing fuel to pass. The ECU calculated this fuel opening to be very precise. As a result, the nozzle finally opens, and fuel is sprayed onto the combustion engine.
After completing a fuel injection cycle, the ECU stops sending the electronic signal to the fuel injector, deactivating the electromagnet. When the electromagnet deactivates, there is nothing pushing the plunger outward, and the nozzle closes, causing the fuel spray to stop.
This mechanism uses by electronic fuel injectors, where an electronic circuit uses to precisely open the valve. Thus no mechanical mechanism uses, despite the fact that the governing principle in both mechanical and electronic fuel injectors is similar.
Conclusion
A fuel injector is an excellent example of engineering that has simplified the problem of delivering the correct amount of fuel for combustion. They have also helped the automobile industry achieve efficiency, better transient throttle response, and cold starting. As the valves allow more fuel to flow for a short period of time, which could not do with carbureted engines.
Also Read: