According to new RBI standards regarding debit and credit cards rules, in July 2022, all credit card applicants will need to provide written authorization. The actual name for the instructions is the Reserve Bank of India [Credit Card and Debit Card – Issuance and Conduct] Directions, 2022.
These guidelines offer a thorough set of instructions. Especially to card issuers regarding the issuance of credit and debit cards, co-branded cards, billing, and telemarketing, among other things.
Who is qualified to grant credit cards?
- The regulations outline which banks have the authority to issue credit and debit cards.
- Most Scheduled Commercial Banks [SCBs] can issue credit cards with a net value of Rs 100 crores.
- RRBs are an exception since they need to collaborate with other banks in order to do so.
- In a similar vein, Urban Cooperative Banks [UCBs] with a net worth of more than Rs 100 crores may provide credit cards under specific circumstances.
For instance, they have permission to only issue credit cards to members. Co-branded credit cards are not permittable, and a UCB’s total unsecured loans and advances cannot amount to more than 10% of its assets.
- Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) registered with the Reserve Bank of India with a minimum net owned fund of Rs 100 crores. And can issue credit cards if they obtain a certificate of registration and authorization to start the company.
Who has the authority to issue debit cards?
Debit cards can be issued by any bank without the RBI’s permission. Debit cards, on the other hand, may only issue to clients with Savings/Current Accounts, not cash/credit/loan account holders.
Notably, banks cannot compel users to obtain a debit card or link it to any other service provided by the bank.
Co-Branding Cards
A co-branded card is one that a retailer of products or services for consumers offers in collaboration with a certain credit card issuer or network. Co-branded cards, frequently have the logos of both the credit card issuer and the retailer. It can be used anywhere that accepts cards from that network. And can offer benefits such as points or item discounts when used with the sponsoring retailer.
A retailer’s business may benefit from co-branded card partnerships since they can draw clients who wouldn’t otherwise be interested in a standard store credit card. Non-profit organizations, as well as other types of organizations or affinity groups, also employ them.

Cards with a co-branding
According to the debit and credit card rules, it is not necessary to obtain RBI authorization to issue co-branded debit or credit cards. Any co-branded credit/debit card must state that it was issued by a co-branding partner. And cannot be marketed as the card’s owner. A partner of this type, limited to marketing and distributing the cards, as well as giving access to the goods and services.
Card authorization in writing
All cards that a card issuer issues must have explicit written approval. Writing has also substituted with other digital methods that incorporate multiple-factor authentication. However, the Department of Regulations of the RBI must inform others of this regulation to others.
Requested Facilities
- Under the new rules related to debit and credit cards, issuers face prohibition from unilaterally upgrading credit cards or raising credit limits. Without the customer’s express permission for any modifications to the terms and conditions.
- No uninvited loans may be made without express permission.
- A card issuer may only send a customer an unsolicited card if it is a replacement or renewal.
- With the customer’s express permission, a new card will also supplied in place of a blocked card. The renewal of cards follows the same rules.
- The issuer will pay an extra penalty equal to twice the amount charged for any charges. That made on an unsolicited card without the customer’s permission.
- The individual in whose name the card will issue may also seek compensation from the RBI Ombudsman.
CIC reporting
One of the rules is that before the activation of the card, the card issuer cannot send any credit information about a new credit card account to the Credit Information Companies (CICs).
The issuer must expressly advise the client that any information needed to be sent to a CIC regarding the cardholder’s credit history and repayment history is being done so in compliance with the Credit Information Companies [Regulation Act, 2005].
If the issuer wants to report a cardholder as a defaulter to a CIC, it must provide them seven days’ notice.
Tokenization
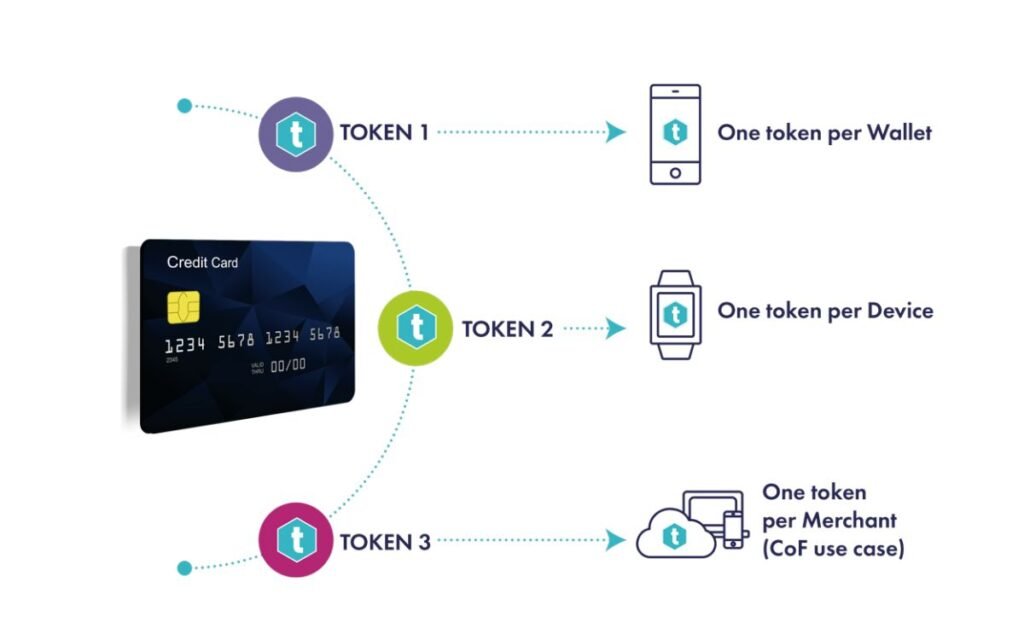
To provide cardholders with a safe and convenient debit card and credit card experience. The RBI has adopted a number of new regulations. The RBI has prohibited merchants and payment gateways from keeping Card on File (CoF), i.e., customer card credentials, on their servers. Urged them to utilize the Card on File Tokenization (CoFT) payment mechanism. I
In order to minimise online frauds of debit and credit card data breaches. The RBI’s primary goal is to provide a security framework for more secure digital transactions.
Due to the incomplete integration of card issuers, card networks, and payment gateways at the time of the RBI’s extension of the deadline for CoFT (from December 2021 to June 30th, 2022). The CoFT deadline was extended by six months by the RBI. E-commerce companies like Amazon, Flipkart, Big Basket, Myntra, etc., as well as payment aggregators and payment gateways like Google Pay, Cashfree, Razor pay, Paytm, etc.
It will no longer allow to store customer card credentials for faster transactions. Once the new rule becomes effective on July 1st, 2022. However, these businesses has a permission to record just a small amount of information for reconciliation reasons. Namely the card issuer’s name and the last four digits of the debit or credit card number.
Customer card credentials will only remain with the ablility to store by issuing banks and card networks such as Visa, MasterCard, Rupay, etc.
The RBI has offered a solution known as Card on File Tokenization (CoFT). That may utilize as a payment mechanism with express customer authorization, as previously described. Let’s examine its nature and operation.
Additional guidelines
It is necessary to provide a one-page Key Fact statement with the credit card application that contains comprehensive information on the card.
During crucial discussions, they must additionally convey the Most Important Terms and Conditions (MITC). These consist of all fees and charges, credit and withdrawal limitations, invoicing information, required minimum payments, processes for default, cancellation, card loss or theft, and grievance resolution.
Telemarketers
According to the debit and credit cards rules, card issuers must make sure that any telemarketers they use to advertise their services. Adhere to the rules set forth by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) and the National Customer Preference Register (NCPR).
Customers may not have contacted by telemarketers outside of the hours of 10 a.m. and 7 p.m. Direct sales or marketing representatives, simply intended to seek or assist consumers. And have not permission to make any choices about card issuance.
Past dues
Additionally, card issuers can only collect fees or submit a credit card account to CICs. If it has been past due for more than three days. Only the amount still owing beyond the due date is subject to penalty interest charges. The entire amount is not subject to penalty interest charges.
Charge adjustments can only be adjustable with one-month advance notice and prospective effect.




