A hereditary blood condition is sickle cell disease. Hemoglobin with flaws is a sign of it. That is the red blood cell protein that transports oxygen to the body’s tissues. Therefore, sickle cell disease prevents the tissues from receiving enough oxygen.
Normal hemoglobin-containing red blood cells are smooth, disk-shaped, and malleable. They can readily pass through the blood vessels. Sticky and stiff cells contain sickle cell haemoglobin. When they run out of oxygen, they take the form of a sickle or a crescent, similar to the letter C. These cells stick to one another and find it difficult to pass via blood arteries. Small blood arteries and the flow of healthy, regular, oxygen-carrying blood may be obstructed by this. The obstruction may be painful.
The lifespan of typical red blood cells is 120 days. However, sickle cells have a short lifespan of 10 to 20 days. Additionally, because of their rigidity and structure, they may eliminate the sickle cells in the spleen. The spleen aids in cleansing infections from the blood. This filter traps and kills sickle cells. You can develop chronic anemia if your body has fewer healthy red blood cells circulating. The spleen has also an effect on the sickled cells. You now have a higher chance of developing infections.
Causes of Sickle Cell Disease
The hereditary condition of a sickle cell has brought on by a gene deficiency.
- Only when two genes—one from the mother and one from the father—have been inherited together that a person can bear sickle cell disease.
- A healthy individual who has the illness in the form of just one gene is called a “carrier.” If a carrier has a child with another carrier, there is a higher probability that the infant will have sickle cell anemia.
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease
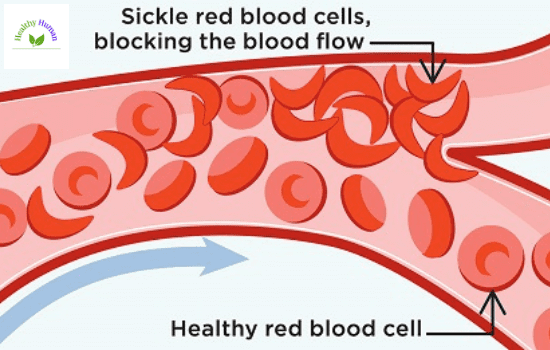
The symptoms and problems related to sickle cell disease are listed below. However, every individual may experience symptoms in a unique way. The following signs and issues might occur:
Anemia
There are fewer red blood cells available in the body. Because sickled cells are short-lived or eliminated. Anemia is the outcome. You may feel lightheaded, out of breath, and exhausted if you have severe anemia.
Pain Crisis or suffering
This happens when sickled cells, are caught in the blood artery, blocking the flow of blood to the affected region. Although it can hurt everywhere, the chest, arms, and legs are where it hurts the most frequently. Young children and infants may have painful toe and finger swelling. Blood flow disruption can also result in tissue death.
Acute Chest Syndrome
When the chest sickles, this happens. This may endanger your life. When the body is under stress from an illness, a fever, or dehydration, it frequently happens suddenly. The sickled cells adhere to one another and stop the passage of oxygen to the lungs’ tiny blood capillaries. It might involve fever, discomfort, and a harsh cough, and it mimics pneumonia.
Splenic sequestration (pooling)
Sickle cells accumulating in the spleen cause crises. If not treated right once, this may result in a precipitous reduction in hemoglobin and be fatal. The increased blood volume may also cause the spleen to expand and hurt. The spleen suffers lasting damage and scarring as a result of recurrent bouts. By the time they reach the age of 8, the majority of kids do not have a functioning spleen, either due to surgical excision or recurrent splenic sequestration. Children lacking a functioning spleen have a high risk of infection. In this group, infections are the leading cause of mortality in children under the age of five.
Stroke
Another abrupt and serious consequence that affects persons with sickle cell illness is this one. The major blood arteries that provide oxygen to the brain, may also get blocked by the malformed cells. Serious brain injury can occur if the blood and oxygen supply to the brain is cut off in any way. A stroke caused by sickle cell anemia increases your risk of a second and third stroke.
Yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mouth calls it jaundice. A prominent indicator and symptom of sickle disease is jaundice. Due to their shorter lifespan than typical red blood cells, sickle cells are degenerating quicker than the liver can remove them from the body. These disintegrated cells produce bilirubin, which gives things their yellow hue, which piles up in the body and causes jaundice.
Priapism
Sickle cells are causing a painful restriction of the blood arteries of the penis. It may lead to impotence if not quickly addressed.
Sickle cell disease symptoms might resemble those of other blood conditions or health issues. For a diagnosis, always consult with your doctor.
Identification of sickle cell anemia
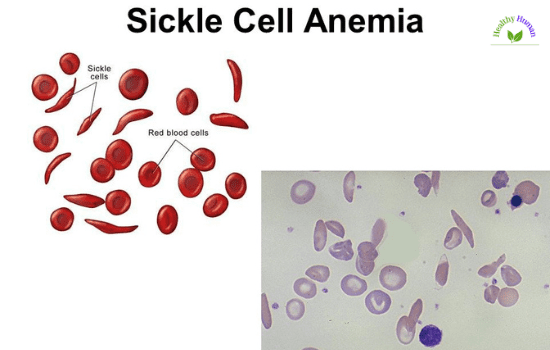
You could get blood and other tests in addition to a thorough medical history and physical examination. In order to start therapy as soon as feasible, several jurisdictions regularly screen neonates for sickle cell. So, the risk of problems may decrease with early identification and treatment.
A blood test called hemoglobin electrophoresis can reveal if a person has sickle cell disease or is a carrier of the sickle cell gene. When deciding on the best course of action for you, your doctor will take into account your age, general health, and other variables.
Treatment for sickle cell disease
Treatment for sickle cell disease must focus on early diagnosis and preventing complications. Infection control, symptom management, and organ damage prevention are the main goals of treatment. Treatment options include:
Pain medicines
For crises related to sickle cell anemia.
Consume a lot of water each day (8 to 10 glasses)
You can do it to stop and handle pain crises. Intravenous fluids may be necessary for some circumstances.
Transfusions of blood.
These might aid in both the treatment and prevention of stroke. In addition, they are utilized to treat crises including splenic sequestration, acute chest syndrome, and persistent discomfort by mixing sickled haemoglobin with regular haemoglobin.
Antibiotics and vaccinations
These serve as an infection preventative.
Vitamin B12
You can avoid serious anemia with folic acid.
Hydroxyurea
Decrease the frequency of pain crises and acute chest syndrome with the use of this medicine. It could also aid in reducing the requirement for blood transfusions. Unknown are the medication’s long-term consequences.
Routine eye examinations
Perform retinopathy screenings with the help of routine eye examinations.
Bone marrow Transplant
Some sickle cell disease patients can also be cured with bone marrow transplants. The choice to undergo this surgery depends on the disease’s severity and the availability of appropriate bone marrow donors. Only in specialist medical facilities can these decisions be made, and they must be discussed with your doctor.
Sickle Cell Disease – A Living Disease
Lifelong treatment is required for sickle cell disease. Living a healthy lifestyle can help to lessen some of the problems of sickle cell disease, even if they may not be completely preventable.
A nutritious diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and protein is crucial, as is drinking a lot of water. So, Decongestants should not be used since they narrow blood arteries and increase the risk of an emergency. High elevations, chilly conditions, swimming in frigid water, and strenuous physical activity are other elements that might cause a crisis.
Get a yearly flu vaccination, wash your hands often, stay away from ill people, and schedule regular dental check-ups to prevent infections.
Conclusion
A blood illness with a hereditary hemoglobin deficiency calls it sickle cell disease. It prevents red blood cells’ hemoglobin from carrying oxygen. Sickle cells have a propensity to aggregate, obstructing tiny blood capillaries and resulting in painful and detrimental effects. When necessary, painkillers, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day, blood transfusions, and pharmaceuticals are used to treat sickle cell disease.
Also read: Steps To Prevent Heart Disease And Stroke




