Welcome to our website Healthy life human. In today’s blog post we will know about Seafood and its health benefits. A wholesome, well-balanced diet must include fish.
What is Seafood?
Excepting mammals but including both freshwater and oceanic organisms, seafood refers to edible aquatic animals. Humans use the majority of non-toxic aquatic creatures for food. Even foods that have the potential to damage consumers, like some blowfish, can be prepared safely. In the next paragraph, you will learn about seafood and its health benefits.
Health benefits of Seafood
After grains, fish and other seafood may be the most important diet for humans, providing 15% of the world’s population’s protein needs. Lean fish muscle has a protein content of 18 to 25 percent by weight, which is comparable to beef or poultry but has a lot fewer calories. One gram of protein can be found in fish for 4 to 10 calories, compared to 10–20 calories per gram of protein in lean meats and up to 30 calories in fatty meats.
The different kinds of seafood are listed below
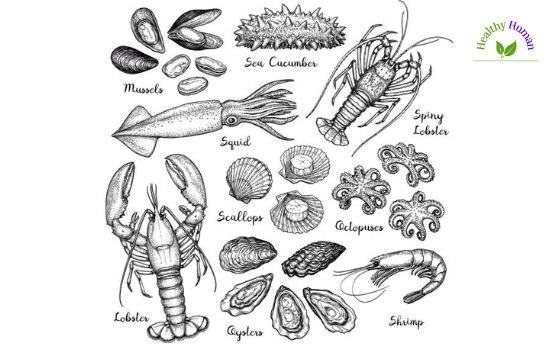
Any type of sea life that people eat is considered seafood. Fish, shellfish, and roe are highly featured. The term “shellfish” refers to a variety of mollusk, crustacean, and echinoderm species. Sea mammals like whales and dolphins have historically been eaten as food. However, this practice is less common now. Edible sea plants such as certain seaweed and microalgae are consumed often as seafood (see the category of edible seaweeds). Any edible aquatic life may be broadly referred to as seafood in North America. However, this is not typically the case in the United Kingdom.
Fish
- Anchovy
- Barramundi
- Billfish
- Carp
- Catfish
- Cod
- Eel
- Flatfish
- Flounder
- Herring
- Mackerel
- Salmon
- Sardine
- Shark
- Sturgeon
- Swordfish
- Tilapia
- Trout
- Tuna
- Whitebait
Shellfish
- Abalone
- Cockles
- Conch
- Crab meat
- Crayfish
- Geoduck
- Krill
- Lobster
- Mussels
- Oysters
- Scallops
- Shrimp
- Sea urchins
- Crustaceans
- Molluscs
Other Seafood
- Edible seaweed
- Jellyfish
- Marine mammals
- Octopus
- Sea cucumber
- Squid
- Whale meat
- Algae
Processed seafood
- Caviar
- Dried fish
- Canned fish
- Cod liver oil
- Cured fish
- Fermented fish
- Fish fillet
- Fish head
- Fish oil
- Fish sauce
- Fish paste
- Fish steak
- Fish stock
- Lutefisk
- Salted fish
- Salted squid
- Shark liver oil
- Shrimp paste
- Smoked fish
- Stockfish
- Surimi
- Roe
Mixed seafood dishes
- Clam dishes
- Crab dishes
- Fish dishes
- Lobster dishes
- Octopus dishes
- Oyster dishes
- Shrimp dishes
- Squid dishes
Benefits of seafood for health

Consuming seafood can lower blood pressure, prevent heart attacks and strokes, and may even help avoid depression. A regular fish diet can reduce heart attack risk by as much as 40%. Omega-3 fatty acids are the secret component of seafood. These healthy fats are rich in fatty fish, including fish, trout, mackerel, sardines, salmon (fresh and tinned), tuna (fresh and canned), and sardines. Just be careful when cooking, as high-temperature pan-frying and deep-frying can degrade omega-3 oils.
All fish are high in protein, low in saturated fat, and rich in vitamin E, an essential enzyme. People with diabetes can benefit from seafood, which can also add calcium to the diet (from the small, soft bones found in some fish) and possibly lower a child’s chance of developing asthma. Depending on how it is made, it has a low-calorie count.
Some people avoid eating shellfish because it may be high in cholesterol, however food cholesterol does not necessarily translate to blood cholesterol. Saturated and trans fats are more harmful to serum (blood) cholesterol than the cholesterol in shellfish, despite the fact that it is still recommended to restrict your intake of cholesterol, especially if you have diabetes or heart disease.
Instead of monitoring cholesterol milligrams, if you’re aiming to lower your blood cholesterol, concentrate on boosting fiber, exercising, and substituting healthy fats for saturated ones.
Seafood still raises concerns about mercury. This metal, which can harm the brain and nerves, is found in some larger fish, including sharks, swordfish, and marlin. These fish should be avoided by expectant mothers and young children, and should only be eaten once a week by everyone else. Luckily, fish with the highest levels of beneficial omega-3 fatty acids also have the lowest mercury levels.
Skin benefits of seafood
Seafood has several health advantages, as we all know. It is the path to clear, smooth skin. Here are some reasons for upping your dietary consumption of fish, oysters, prawns, and other seafood.
You’ve probably heard that seafood is really healthy and gives you beautiful skin. Protein, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and other nutrients are added to it. Seafood preserves the shine, smoothness, and health of your skin in addition to offering a number of health advantages. Learn why including seafood in your diet is a good idea by reading about it.

Aging symptoms
One of the simplest ways to minimize the appearance of wrinkles, fine lines, crow’s feet, dull, dry skin, and pigmentation is by eating seafood. It contains vitamin E, which aids in your ability to seem young. This is why the majority of skincare products include this advantageous skin ingredient.
Aging symptoms
UV rays are extremely damaging to the skin and can lead to sunburn, pigmentation, wrinkles, and, in extreme cases, skin cancer. However, seafood with a sufficient level of fish oil helps to shield the skin from damaging UV rays.
Improves skin tone
People who regularly consume seafood tend to have light skin and pearly white hair. The omega-3 fatty acids make the skin soft and supple by preserving the production of natural oil in them. Additionally, seafood increases circulation, giving you skin that is beautiful and clean.
Important things to know about seafood
They are a wonderful source of vitamins, lean protein, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health.
Eating the appropriate kind of fish during pregnancy or while nursing benefits the health of the child.
The entire public is advised by the dietary recommendations to consume at least eight ounces of seafood per week.
According to the recommendations, women who are expecting or nursing should consume at least eight ounces and up to 12 ounces of mercury-free seafood per week.
Kids should consume less food.
Our rivers may get contaminated with chemicals as a result of mining, agriculture, spills, poor waste management, and the use of coal and other fuels.
Mercury and PCBs are two chemicals that should be avoided.
Although eating fish provides nutritional advantages, there are also some risks.
Both the water and the food consumed by fish can contain these pollutants.
When people consume seafood that contains high concentrations of PCBs and mercury, these substances may eventually get into their systems.
The brain and neurological system might suffer damage from high mercury and PCB levels.
Children, newborns, and fetuses can all be adversely affected by mercury.
Other negative health impacts from PCBs include cancer.
Some fish species may have substantially higher concentrations of a pollutant in the same area than other fish species.
Additionally, a fish species may have substantially higher concentrations of a pollutant in one region than in another.
By simply just eating or looking at a fish, it is impossible to tell its the chemical content.
Thankfully, there are simple steps you can take to lower your risk and take advantage of the health benefits of eating fish.
Before cooking fish, it’s important to clean and prepare it.
Before cooking, remove the skin, trim the exposed fat, and fillet the fish.
The amount of several compounds in the fish’s skin, fat, and internal organs is higher than it is in the meat.
When creating soups or stews, it’s better to avoid using certain fish portions or whole fish.
Additionally, you can bake or broil the fish while allowing the cooking fluids to drain, then discard them.
The juices may contain higher chemical concentrations.
Remove the internal organs and clean the body cavity of crabs and lobsters before cooking.
Whole crabs or lobsters can be boiled or steamed instead of being fried or broiled; the cooking liquid should be discarded.
Although there are certain possible concerns to take into account, eating fish has many health advantages.
You won’t gain from the nutrients that fish can offer if you completely avoid eating it.




